Example Of Food Chain In An Intertidal Zone And Estuarine Ecosystem
Fjord -- valleys deepened by glaciers and invaded by the sea. Click again to see term.

Intertidal Zone Of Estuaries Defined Habitat Functions Of Estuarine Marsh Areas Bright Hub
The water is separated into zones going from the light photic zone to the slightly spookier twilight zone to the pitch-black midnight zone.
Example of food chain in an intertidal zone and estuarine ecosystem. The oceans food chain starts with light. Lobsters eat clams 1. The intertidal zone marks the area where the ocean and land meet.
Illustration by National Geographic Education. All food chains and food webs in estuaries start with the sun which provides energy for plants and other producers. An example of this is round worms on fish.
Round worms sap the nutrients from the intestines of fish. -They make their own food by converting the energy from the sun into chemical energy. Elly fish eat sea snails.
The mussel is then eaten by an ochre star which may be eaten by a gull or a sea otter. Semi-enclosed coastal bays in which freshwater and sea water mix. Animation shows low tide medium tide high tide and very high tide.
Examples of nearly every type of estuarine habitat exist along the. A healthy ecosystem must have suitable environmental conditions to support the growth of abundant producers. For consumers use oysters horseshoe crabs birds and sharks as examples.
Barnacles mussels and kelps can survive in this environment by anchoring themselves to the rocks. In this exercise the producers are phytoplankton found in rich estuary waters. Barnacles and mussels can also hold seawater in their closed.
Algae and other plants are eaten by plant-eating zooplankton. Tap again to see term. An example would be the use of the chemical superphosphate which could lead to the increase in nutrient levels and fuel the growth of algae in estuaries- Industries like fishing and oyster farming can impact the water quality and also the movement of water in estuaries.
The common crab and shannys populations would have the greatest increase in size since the herring gull was their only predator and it has been removed from the ecosystem. In this image the green arrows mark a producer the blue a primary consumer the pink a secondary consumer the brown a tertiary consumer and the red denotes apex predators. The herring gull is an example of a keystone species.
Guide the pupils while they are doing the activity. The intertidal zone can be found in. Over-fishing and habitat loss reduces the amount of fish in the ocean and disrupts the food chain.
Distribute the activity card containing the specific instructions on how they are going to construct the. Because the worm benefits from receiving the food and the fish suffers it is an example of parasitism. Clams eat zooplankton 2.
Classification based on climate and geology. 200 μgml macrofauna including 120 μgml subsurface deposit feeders 50 μgml meiofauna 20 μgml Foraminifera 1 μgml Ciliata and Flagellata and 100 μgml bacteria. By stealing their nutrients they steal the fishs food and are able to feed themselves.
Larger marine life such as seals sea lions and fish find foraging for food ideal at high tide in the intertidal zone while a large variety of shorebirds looking. This unique ecosystem maintains an important balance for the food chain supplies erosion protection and serves as an indicator for climate change. -They provide energy and nutrients to other organisms.
Intertidal zones of rocky shorelines host sea stars snails seaweed algae and crabs. Cut-outs of animals in the marine ecosystem cut-outs of arrows. Food chain and food web in the estuaries and intertidal zones.
Habitats associated with estuaries include salt marshes mangrove forests mud flats tidal streams rocky intertidal shores reefs and barrier beaches. -Mainly green plants algae or maicroorganisms that undergo photosynthesis. ATP-biomass is discussedMeiofauna and Foraminifera.
This plankton is eaten by larger carnivorous plankton. This is another example of an imaginary marine food web for the rocky intertidal zone. If he was removed then the edible crab worm common prawns and shanny populations would grow.
Tap card to see definition. These are eaten by a mussel barnacle or other marine invertebrate. A single tide pool contains many food chains.
Up to 10 cash back From bibliographic data the biomass correlations organic dry weight are constructed for the subsurface layer of a hypothetical 30 m deep silty sand station.
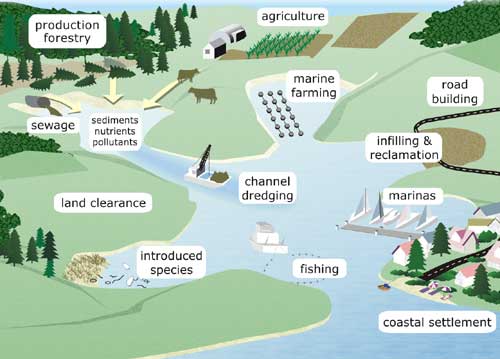
Threats To Estuaries Estuaries

The Alphabet Soup Of Vertical Datums Why Mhhw Is Mmm Mmm Good Estuary Tidal Zone Science

Estuaries Where The River Meets The Sea Learn Science At Scitable
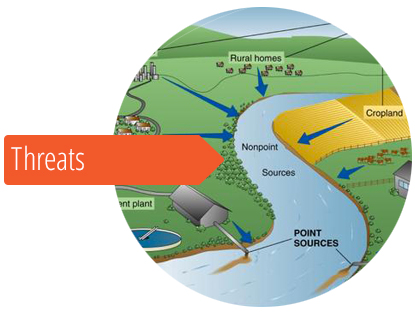
Threats To Estuaries Estuaries

Marcia S Science Teaching Blog Teaching Life Zones In The Ocean Ocean Zones Oceanography Ocean

The Inter Tidal Zone Period 3 By Ken Rosenberg Katie Collins Jen Jenson Tidal Zone Zone Collins
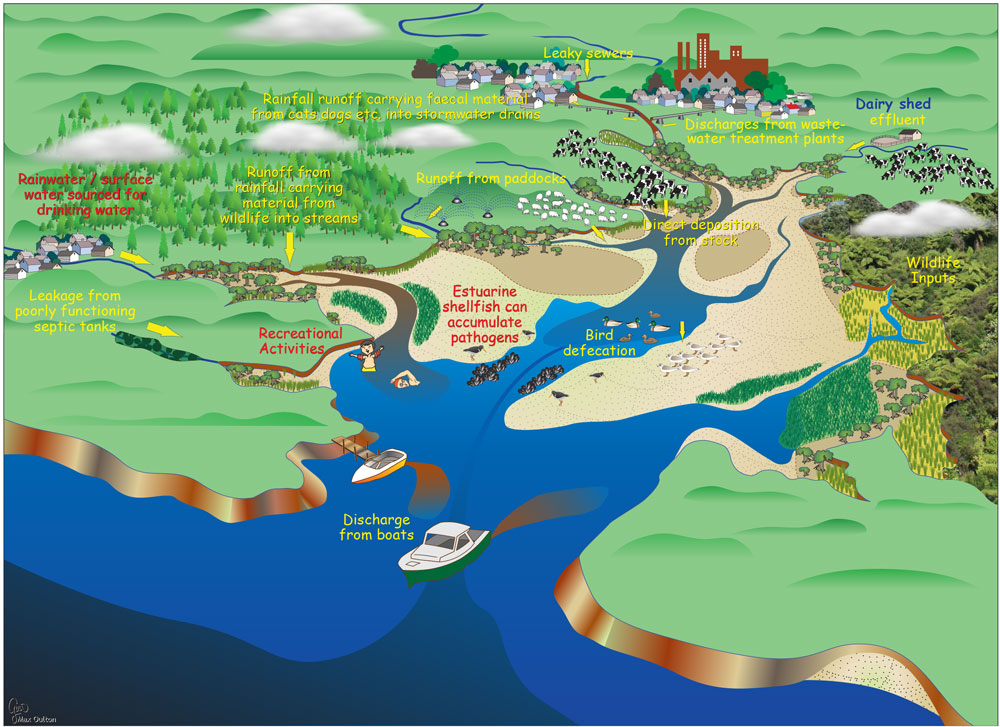
Threats To Estuaries Estuaries
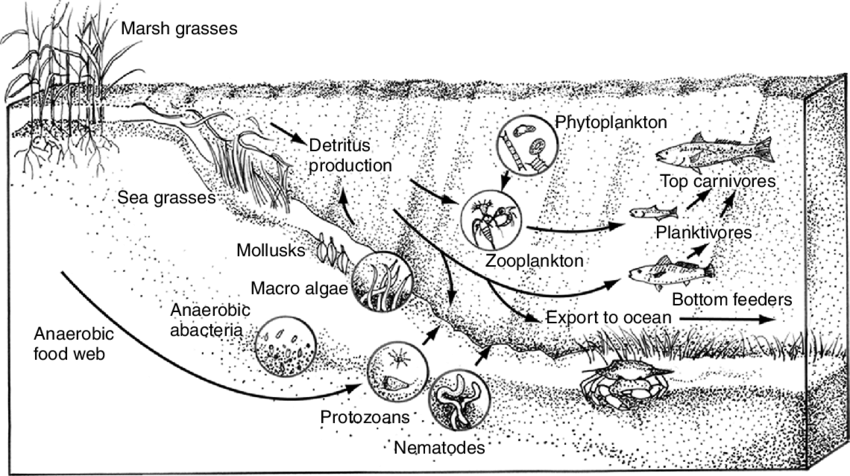
4 Food Web Diagram For A Typical Estuarine Ecosystem Showing Some Download Scientific Diagram

2 Idealized Cross Section Through A Typical Estuary Showing Vertical Download Scientific Diagram

By Nicole Fazio See Http Www Nicolefazioillustration Com Illustration Illustration Illustration Art Art

The Chesapeake Bay Exploring Nature Educational Resource Chesapeake Chesapeake Bay Biomes

Estuarine Ecosystem Services Are Underpinned By Multiple Ecosystem Download Scientific Diagram
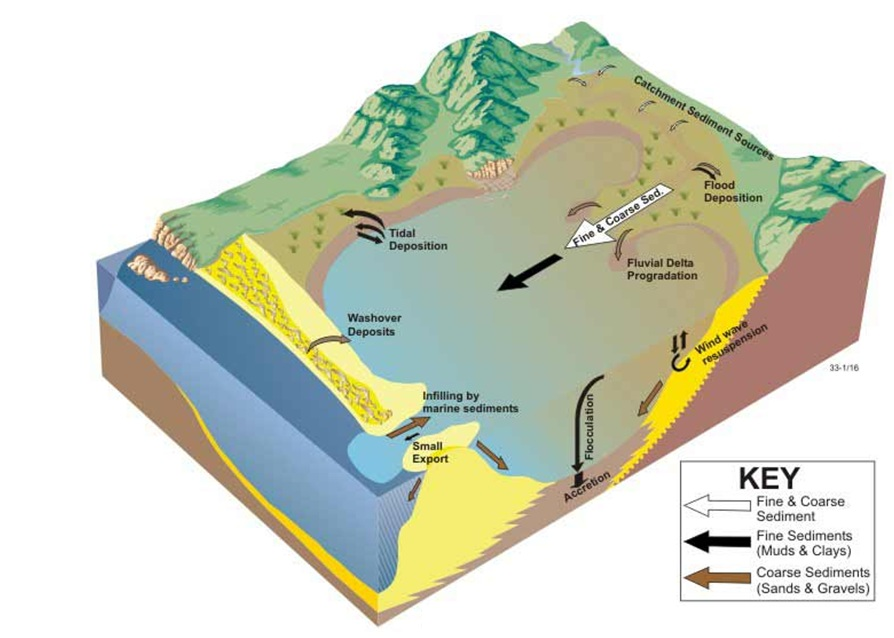
Estuarine Environment Ecoshape

Healthy Estuaries Provide Diverse Ecosystem Services Relative To Their Download Scientific Diagram

Estuarine Food Web Food Web Wetlands Activities Estuary

Each Ecological Niche Has A Food Web But Each Is Dependent On The Other To Stay Healthy Food Web Coastal Ecosystems Trophic Level
Conceptual Diagram Of Shifts In Estuarine Ecosystem Functionality From Download Scientific Diagram

Post a Comment for "Example Of Food Chain In An Intertidal Zone And Estuarine Ecosystem"